Gum Diseases & Treatment
- What are commonly observed gum diseases?
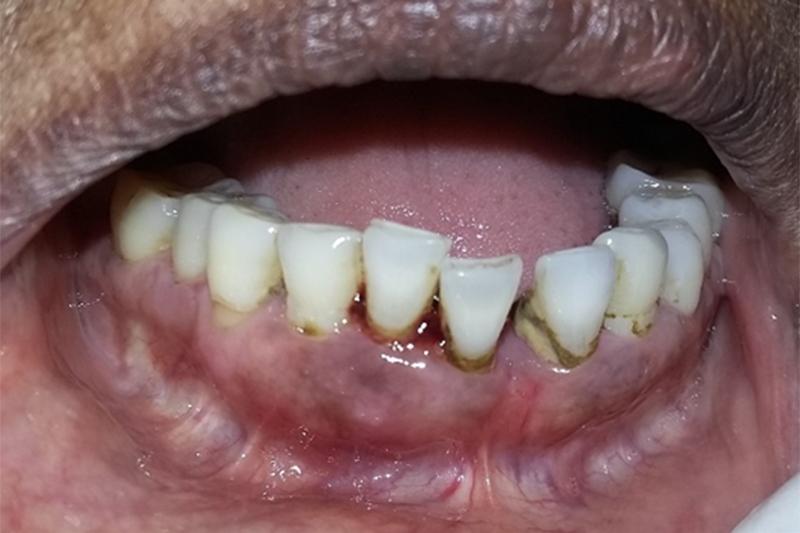
Commonly observed gum diseases include gingivitis (inflammation of the gums), periodontitis (infection and inflammation of the gums and supporting structures of the teeth), and periodontal abscesses (localized infections in the gums or supporting bone).
- How are gum diseases treated?
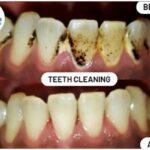
The treatment of gum disease depends on the severity and type of the disease. In the early stages, gingivitis can be treated with improved oral hygiene practices such as regular brushing, flossing, and professional dental cleanings. More advanced gum disease such as periodontitis may require more intensive treatment such as scaling and root planning (deep cleaning), antibiotics, or surgery in severe cases. It’s important to see a dentist or periodontist for proper diagnosis and treatment of gum disease.
- What is gingivitis and how is it treated?
Gingivitis is a type of gum disease that involves inflammation of the gums. It is typically caused by a buildup of plaque on the teeth, which can lead to bacterial infections and irritation of the gums. Common symptoms of gingivitis include red, swollen, and tender gums that may bleed when brushed or flossed. In most cases, gingivitis can be reversed with proper oral hygiene practices such as regular brushing and flossing, and professional dental cleanings. However, if left untreated, it can progress to more serious forms of gum disease such as periodontitis.
- What is periodontitis and how it is treated?
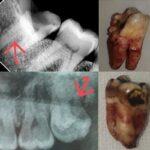
Periodontitis is an advanced stage of gum disease that involves both inflammation of the gums and damage to the supporting structures of the teeth such as the bone and connective tissues. It is typically caused by a buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth, which can lead to bacterial infections and inflammation. Common symptoms of periodontitis include red, swollen, and bleeding gums, as well as receding gums, loose teeth, and bad breath.
The treatment of periodontitis may involve a combination of procedures such as scaling and root planing (deep cleaning), antibiotics, and sometimes surgery. The goal of treatment is to remove the bacteria and infected tissues from the affected area and promote the regeneration of healthy gum tissue and bone. In addition to professional treatment, it’s important for individuals with periodontitis to maintain good oral hygiene practices such as regular brushing and flossing, and to schedule regular dental cleanings and checkups to monitor the progress of the disease.
- What is periodontal abscesses and how is it treated?
A periodontal abscess is a type of localized infection in the gums or supporting bone that results from a bacterial infection. It can occur in individuals with advanced periodontitis, or as a result of injury to the gums or teeth. Symptoms of a periodontal abscess may include pain, swelling, redness, and discharge of pus.
The treatment of a periodontal abscess typically involves drainage of the abscess and removal of the bacteria and infected tissue from the affected area. This may be accomplished through procedures such as incision and drainage or root canal therapy, depending on the location and severity of the abscess. Antibiotics may also be prescribed to control the infection and prevent it from spreading.
In addition to professional treatment, it’s important for individuals with periodontal abscesses to maintain good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, to prevent further infection. It’s also important to schedule regular dental cleanings and checkups to monitor the health of the gums and teeth.
- What happens if gum diseases are not treated?
If gum diseases such as gingivitis and periodontitis are not treated, they can progress and lead to more serious health problems. If left untreated, gum disease can cause damage to the bone and soft tissue that support the teeth, which can lead to tooth loss. In addition, the bacteria associated with gum disease can enter the bloodstream and travel to other parts of the body, potentially increasing the risk of other health problems such as heart disease, stroke, respiratory infections, and diabetes.
It’s important to treat gum disease as early as possible to prevent further damage and complications. Regular dental checkups and cleanings can help to detect and treat gum disease in the early stages before it progresses. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices such as regular brushing and flossing, and avoiding risk factors such as smoking, can also help to prevent gum disease.