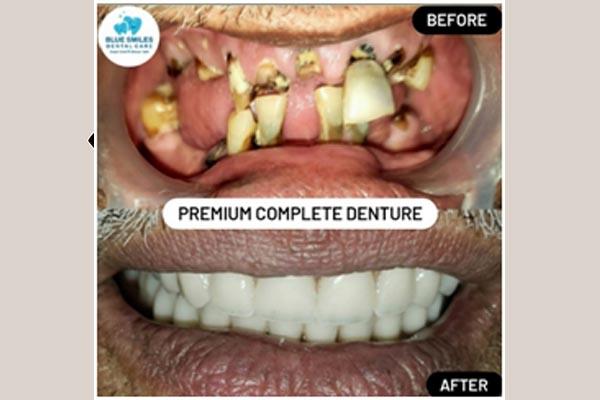
- What are dentures?
Dentures are prosthetic devices designed to replace missing teeth and gums. They are commonly made of acrylic resin, nylon, or metal, and are designed to fit snugly over the gums to provide a comfortable and functional replacement for natural teeth. Dentures can be complete, meaning they replace all of the upper or lower teeth, or partial, meaning they only replace some of the missing teeth. They can also be fixed, meaning they are attached to the remaining natural teeth or dental implants, or removable, meaning they can be taken out and put back into the mouth. Dentures are typically used to improve chewing ability, speech, and appearance, and can be a good solution for people who have lost all or most of their natural teeth.
- When are dentures prescribed?
Dentures are typically prescribed when a person has lost all or most of their natural teeth due to injury, disease, decay, or advanced age. They can be used to replace one or multiple missing teeth, and can be a good solution for people who want to improve their chewing ability, speech, and appearance. In some cases, dentures may be prescribed as a temporary solution while a person waits for dental implants to heal, or as a permanent solution for people who are not suitable candidates for dental implants or other tooth replacement options.
The decision to prescribe dentures will depend on several factors, including the patient’s overall health, the number and location of missing teeth, and the patient’s personal preferences and goals. The dentist will assess the patient’s situation and work with them to develop a treatment plan that meets their individual needs and goals.
- Difference between full and partial dentures
Full dentures and partial dentures are two different types of dentures that are used to replace missing teeth.
Full dentures are designed to replace all of the upper or lower teeth, and they rest on the gums that cover the jawbone. They are typically made of acrylic resin or nylon, and they are designed to fit snugly over the gums to provide a comfortable and functional replacement for natural teeth. Full dentures are held in place using natural suction or dental adhesives, and they can be removed for cleaning and maintenance.
Partial dentures, on the other hand, are designed to replace only some of the missing teeth. They are typically made of a metal framework with acrylic resin or nylon teeth, and they are designed to fit snugly between the remaining natural teeth. Partial dentures are held in place using metal clasps that attach to the adjacent natural teeth, and they can be removed for cleaning and maintenance.
The choice between full and partial dentures will depend on several factors, including the number and location of missing teeth, the health of the remaining natural teeth, and the patient’s personal preferences and goals. The dentist will assess the patient’s situation and work with them to determine the best solution for their individual needs and goals.
- Procedure for fixing dentures
The procedure for fixing dentures will vary depending on whether the dentures are complete or partial, and whether they are fixed or removable. Here is a general overview of the steps involved in fixing dentures:
- Consultation: The first step is to schedule a consultation with a dentist or prosthodontist. During this appointment, the dentist will examine the mouth, take X-rays and impressions of the gums and teeth, and discuss the patient’s goals and expectations for their denture treatment.
- Design and fabrication: Based on the impressions and X-rays, the dentist will design and fabricate the dentures to fit the patient’s mouth precisely. This may involve several appointments to ensure the dentures fit properly and are comfortable.
- Try-in: Before the final dentures are made, a try-in appointment will be scheduled to allow the patient to try on the dentures and provide feedback on the fit and appearance.
- Delivery and adjustment: When the dentures are ready, the dentist will fit them in the patient’s mouth and make any necessary adjustments to ensure a proper fit and comfort.
- Follow-up: After the dentures are fixed, the patient will need to schedule follow-up appointments to monitor the fit and comfort of the dentures, and to make any necessary adjustments.
For fixed dentures, the procedure will involve additional steps, such as placement of dental implants and fabrication of a custom abutment and denture. The dentist will provide a detailed explanation of the steps involved in fixing the dentures and what to expect during the recovery process.
- Pros and cons of dentures
Dentures can be a good solution for people who have lost all or most of their natural teeth, but like any dental treatment, they have both advantages and disadvantages. Here are some of the pros and cons of dentures:
Pros:
- Improved appearance: Dentures can replace missing teeth and restore a natural-looking smile, which can improve self-esteem and confidence.
- Improved chewing ability: Dentures can restore the ability to chew food properly, which can improve digestion and overall health.
- Improved speech: Dentures can restore the ability to speak clearly, which can improve communication and social interactions.
- Convenient: Removable dentures are easy to clean and maintain, and they can be taken out of the mouth for cleaning and overnight storage.
Cons:
- Adjustment period: It may take some time for the patient to get used to wearing dentures, and they may experience discomfort or irritation during the adjustment period.
- Maintenance: Dentures require regular cleaning and maintenance, and they may need to be repaired or replaced over time.
- Slippage: Removable dentures may slip or shift in the mouth, which can be uncomfortable and embarrassing.
- Reduced sense of taste: Dentures can interfere with the sense of taste, making food less enjoyable.
- Cost: Dentures can be expensive, and they may not be covered by insurance or may only be partially covered.
It is important to consider the pros and cons of dentures and to discuss them with a dentist or prosthodontist before deciding if they are the right solution for your individual needs and goals. The dentist can provide a detailed explanation of the benefits and limitations of dentures, and can help you determine if they are the best option for you.
- How long does dentures last?
The lifespan of dentures can vary depending on several factors, such as the quality of the materials used, the frequency of use, the patient’s oral hygiene habits, and the patient’s overall oral health. On average, dentures can last anywhere from 5 to 10 years, but some may last longer with proper care and maintenance.
It is important to note that dentures can become worn or damaged over time, and they may need to be repaired or replaced as a result. The denture material can also become stained or discolored, which can affect the appearance and functionality of the dentures. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings can help extend the lifespan of the dentures, and the dentist can recommend replacement or repair when necessary.
In general, it is recommended to have a complete evaluation of your dentures at least once a year to ensure they are still functioning properly and to catch any potential issues early on. The dentist can also make any necessary adjustments to ensure a proper fit and comfort.
- How to clean dentures regularly
Cleaning dentures regularly is important to maintain their appearance, prevent bad odors, and prevent oral infections. Here are some steps for cleaning dentures:
- Rinse: After removing the dentures from the mouth, rinse them thoroughly with cool water to remove any loose food particles or debris.
- Clean: Use a denture cleansing solution, to gently clean the dentures, being careful not to damage the denture material. Use a soft-bristled brush to scrub the dentures, paying special attention to the surfaces that come in contact with the gums.Some recommended cleaning solutions include denture cleaning tablets, white vinegar, or baking soda and water.
- Rinse again: Rinse the dentures thoroughly with cool water to remove any cleansing solution residue.
- Soak: Soak the dentures in a cleaning solution overnight to help remove any stains and disinfect the denture material.
- Brush: Before wearing the dentures, use a soft-bristled brush to gently scrub the dentures again to remove any remaining residue.
- Store: When not in use, store the dentures in a clean and dry place, such as a denture case or a cup of water. Do not leave the dentures in a dry environment, such as near a heat source, as this can cause the denture material to warp.
It is also important to clean the mouth and gums regularly, even if you have dentures. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to gently brush the gums, tongue, and roof of the mouth, and use a mouth rinse to freshen the breath.
It’s recommended to avoid using harsh chemicals, abrasive cleaners, or hot water to clean dentures, as these can damage the denture material and affect its fit and appearance. If you have questions about cleaning your dentures, consult your dentist for personalized recommendations and advice.