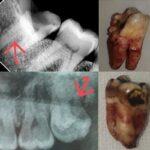
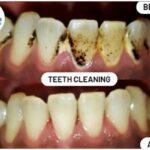
Poor oral health can lead to a variety of serious health problems, some of which can be life-threatening. Here are some examples:
- Cardiovascular disease: The bacteria associated with gum disease have been linked to the development of heart disease and stroke.
- Endocarditis: This is a potentially life-threatening infection of the inner lining of the heart (endocardium) caused by bacteria from the mouth.
- Pneumonia: The oral bacteria can also be aspirated into the lungs and cause pneumonia, which can be a serious condition, especially in people with compromised immune systems.
- Diabetes: People with poor oral health are more likely to develop diabetes and have difficulty managing the disease.
- Osteoporosis: Gum disease can lead to bone loss and increase the risk of osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones and makes them more likely to break.
It’s important to maintain good oral health by brushing and flossing regularly, visiting the dentist regularly, and following a healthy diet to prevent these and other health problems associated with poor oral health.
- Oral health in diabetes patients
People with diabetes are at an increased risk for oral health problems due to elevated blood sugar levels and impaired immunity. Here are some of the common oral health issues that can affect people with diabetes:
- Gum disease: People with diabetes are more prone to developing gum disease, which can cause red, swollen, and bleeding gums. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and other health problems.
- Thrush: People with diabetes are more likely to develop thrush, a fungal infection of the mouth that causes white, painful patches on the tongue and cheeks.
- Dry mouth: High blood sugar levels can lead to a decrease in saliva production, which can cause dry mouth, making it more difficult to maintain good oral hygiene.
- Slow healing: People with diabetes may take longer to heal after oral surgery or injury due to impaired blood flow and reduced immunity.
It’s important for people with diabetes to maintain good oral hygiene, including brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting the dentist regularly. Good glycemic control can also help reduce the risk of oral health problems. People with diabetes should talk to their dentist and healthcare provider about their oral health and the best ways to maintain it.