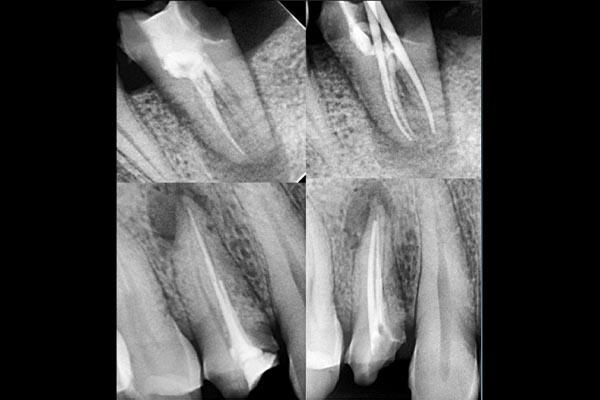
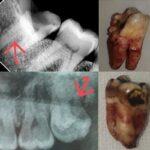
Root canal treatment (also known as endodontic therapy) is a dental procedure performed to remove infected or damaged tissue from inside a tooth (the “root canal”) and to clean and seal the canal to prevent re-infection. The goal of root canal treatment is to save a severely damaged or infected tooth, instead of extracting it. During the procedure, the dentist removes the diseased tissue, fills the canal with a material called gutta-percha, and seals it with a filling or crown.
- When should I go for root canal treatment?
You should consider a root canal treatment if you have:
- Severe toothache or sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures
- Swelling or tenderness in the gums near the affected tooth
- A visible bump or pimple on the gums near the affected tooth
- Darkening or discoloration of the affected tooth
- Tooth decay that has reached the inner pulp of the tooth
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to visit a dentist as soon as possible to avoid further damage or the spread of infection. Early treatment can often save the tooth and prevent the need for extraction.
- What is the procedure for root canal treatment?
The procedure for a root canal treatment typically involves the following steps:
- Anesthesia: The dentist will numb the area around the affected tooth to minimize discomfort.
- Access: An opening is made through the top of the tooth to access the root canal.
- Cleaning: Using special instruments, the dentist will remove the infected or damaged pulp from the root canal. The canal is then thoroughly cleaned and shaped to prepare for filling.
- Filling: The cleaned and shaped root canal is filled with a material called gutta-percha. This seals the canal and helps to prevent re-infection.
- Sealing: The opening in the tooth is then sealed with a filling or a temporary filling may be placed if a crown is to be added later.
- Final restoration: In most cases, a permanent crown is placed over the treated tooth to protect it and restore its function.
The entire procedure usually takes one or two visits to the dentist and may cause some discomfort during and after the treatment, but this can be managed with pain medication prescribed by the dentist.
- When is a root canal treatment prescribed?
A root canal treatment is prescribed when the pulp (soft tissue inside the tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels) becomes infected or inflamed. This can happen as a result of:
- Tooth decay: When a cavity is left untreated, it can spread to the pulp and cause an infection.
- Trauma: A physical injury to a tooth, such as a chip or crack, can damage the pulp and lead to an infection.
- Repeated dental procedures: Having multiple procedures done on the same tooth can increase the risk of pulp damage and infection.
- Gum disease: Advanced gum disease can cause the supporting tissues around the teeth to break down, leading to an infection in the pulp.
The goal of a root canal treatment is to remove the infected or inflamed pulp, clean the inside of the tooth, and seal it to prevent re-infection. This procedure can save a damaged tooth and prevent the need for extraction.
- Is root canal treatment painful?
Root canal treatment is often performed to relieve pain and discomfort caused by an infected or inflamed pulp. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia to numb the area around the affected tooth, so most patients report little to no pain during the treatment.
After the procedure, some patients may experience mild to moderate discomfort or sensitivity, which can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription pain medication as advised by your dentist. In some cases, temporary discomfort or swelling may occur, but this should subside within a few days.
Overall, root canal treatment is typically less painful than the toothache or sensitivity that led to the need for the procedure. Most patients are able to return to their normal activities immediately after the procedure.
- Why should I save teeth rather than extracting?
There are several reasons why it is generally recommended to save teeth instead of extracting them:
- Maintains natural tooth structure: Keeping your natural teeth helps to maintain the normal biting and chewing function, and also helps to preserve the natural shape of your jaw and face.
- Prevents adjacent teeth from shifting: When a tooth is extracted, the adjacent teeth may shift and change position, which can affect the bite and cause other problems.
- Prevents bone loss: The roots of teeth stimulate the jawbone and help to maintain its density. When a tooth is extracted, the bone in the area can start to resorb, leading to bone loss over time.
- Cost-effective: Extracting a tooth and replacing it with a bridge or implant can be more expensive and time-consuming than saving the tooth with a root canal treatment.
- Avoids additional procedures: Extracting a tooth often requires additional procedures, such as bone grafting or sinus lifts, to prepare the site for a replacement.
Root canal treatment is a highly effective way to save a damaged or infected tooth and prevent the need for extraction. With proper care, a tooth that has had a root canal treatment can last a lifetime.
- Why is root canal treatment suggested instead of filling?
Root canal treatment (RCT) is often suggested as a means of filling because it serves two purposes:
- Removes infected or damaged tissue: The goal of RCT is to remove infected or damaged tissue from the pulp of a tooth and to clean and shape the root canals to prevent re-infection.Root canal treatment (RCT) is suggested instead of just a filling in cases where the pulp (the soft tissue inside the tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels) has become infected or inflamed. A filling is typically used to repair a cavity or small crack in a tooth, but when the pulp is damaged, it needs to be removed and the root canal needs to be cleaned and sealed to prevent re-infection.RCT is necessary when the pulp is damaged because, if left untreated, the infection can spread and cause significant pain, swelling, and other symptoms. It can also lead to the loss of the affected tooth, which can have a negative impact on oral health and quality of life.
- Fills the root canal: After the infected or damaged tissue has been removed, the cleaned and shaped root canal is filled with a material called gutta-percha. This seals the canal and helps to prevent re-infection.By removing the infected or damaged tissue and filling the root canal, RCT can save a damaged or infected tooth and prevent the need for extraction. This helps to maintain the normal biting and chewing function, preserve the natural shape of the jaw and face, and prevent adjacent teeth from shifting.
- Complications after root canal treatment
Root canal treatment is generally a safe and effective procedure for saving a damaged or infected tooth. However, as with any medical procedure, there is a small risk of complications. Some possible complications after root canal treatment include:
- Pain or discomfort: Some patients may experience mild to moderate discomfort or sensitivity after the procedure, which can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription pain medication.
- Infection: In rare cases, the tooth may become re-infected after the procedure. This can be caused by a failure to properly clean the root canal, or by a problem with the filling material used to seal the canal.
- Nerve damage: In rare cases, the nerve that supplies sensation to the tooth may be damaged during the procedure. This can result in numbness or tingling in the lip, tongue, or face.
- Fractured tooth: In rare cases, the tooth may fracture after the procedure, especially if it was weakened prior to the procedure.
- Sinus problems: If the tooth being treated is located near the sinus, there is a small risk of sinus problems after the procedure, such as sinusitis or sinus pain.
In general, the risk of complications after root canal treatment is low, and most patients experience a full recovery without any issues. If you experience any problems after the procedure, it is important to contact your dentist as soon as possible for an evaluation.